[最も人気のある!] greenhouse gas effect 100583-Greenhouse gas effect on atmosphere
Multiple gases contribute to the greenhouse effect that sets Earth's temperature over geologic time Small changes in the atmospheric concentration of these gases can lead to changes in temperature that make the difference between ice ages when mastodons roamed the Earth, and the sweltering heat in which the dinosaurs livedThe Greenhouse Gas Impact of GTL – An Industry View – Submission to CARB November 08 Property of Sasol Chevron Holdings Limited and Sasol Chevron Consulting Limited – to be reproduced, and used only in accordance with the terms approved by, and with the written permission of said companies Table of Contents 1 The impact of food on greenhousegas (GHG) emissions can slip under the radarIn a survey in Britain last year, the share of respondents saying that
Causes And Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouse gas effect on atmosphere
Greenhouse gas effect on atmosphere- Data will also be analysed to quantify the economic and environmental benefits of improvements in feed efficiency and reduced greenhouse gas emissionsWater vapor The most abundant greenhouse gas, but importantly, it acts as a feedback to the climate Water vapor increases as the Earth's atmosphere warms, but so does the possibility of clouds and precipitation, making these some of the most important feedback mechanisms to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide (CO 2) A minor but very important component of the




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia
A cow does on overage release between 70 and 1 kg of Methane per year Methane is a greenhouse gas like carbon dioxide (CO2) But the negative effect on the climate of Methane is 23 times higher than the effect of CO2 Therefore the release of about 100 kg Methane per year for each cow is equivalent to about 2'300 kg CO2 per yearGreenhouse Effect Teaching Box Goal Students will learn how greenhouse gases temporarily trap heat within Earth's atmosphere, warming our planet via Engage Ask your students what they have heard about the greenhouse effect Ask them to explain whether they think it Some of the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere are caused by humans Whenever we burn anything, such as— gasoline in our cars and trucks, jet fuel in our planes, coal in our factories or powerplants, trees to clear the land for farming —we pollute our atmosphere with carbon dioxide and carbon monoxide Although carbon monoxide does not
Include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous Greenhouse gases are gases that can trap heat They get their name from greenhouses A greenhouse is full of windows that let in sunlight That sunlight creates warmth The big trick of a greenhouse is that it doesn't let that warmth escape That's exactly how greenhouse gases act They letThe AGGI in was 147, which means that we've turned up the warming influence from greenhouse gases by 47% since 1990;
With increasing levels of greenhouse gases causing our climate to change, it is important to understand exactly where these gases come from and how they disperse in the atmosphere A new dataset, produced by the European Space Agency's Climate Change Initiative, provides a detailed view of carbon dioxide and methane – two of the most important humanHow do greenhouse gases affect the climate?It took ~240 years for the AGGI to go from 0 to 1, ie, to reach 100%, and 30 years for it to increase by another 47% In terms of CO 2 equivalents, the atmosphere in contained 504 ppm, of which 412 is CO 2 alone The rest comes from other



Greenhouse Gases



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Teaching Wiki
Food production is a major driver of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, water and land use, and dietary risk factors are contributors to noncommunicable diseases Shifts in dietary patterns can therefore potentially provide benefits for both the environment and health However, there is uncertainty about the magnitude of these impacts, and the dietary changes necessary to The greenhouse effect is the way in which heat is trapped close to Earth's surface by "greenhouse gases" These heattrapping gases can be thought of as a blanket wrapped around Earth, keeping the planet toastier than it would be without them Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxides Greenhouse gases include water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone The major greenhouse gases are water vapor, which causes about 3670% of the greenhouse effect on Earth




Causes And Greenhouse Effect




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach
Greenhouse gas, any gas that has the property of absorbing infrared radiation (net heat energy) emitted from Earth's surface and reradiating it back to Earth's surface, thus contributing to the greenhouse effect Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are the most important greenhouse gases (To a lesser extent, surfacelevel ozone, nitrous oxides, and fluorinated The US Environmental Protection Agency estimates that in 18, methane emissions from natural gas and petroleum systems and from abandoned oil and natural gas wells were the source of about 29% of total US methane emissions and about 3% of total US greenhouse gas emissions 1 The oil and natural gas industry takes steps to prevent naturalFor thousands of years, the global greenhouse gas supply was essentially stable Natural processes removed as much carbon from the atmosphere as they released Human activities like burning fossil fuels have added huge quantities of carbon dioxide, methane and nitrous oxide to our atmosphere, creating a "greenhouse effect" that traps energy from the sun and causes Earth's




Causes Facts Climate Change Vital Signs Of The Planet



Reducing The Impacts Of Greenhouse Gases Springerlink
The natural greenhouse effect is a phenomenon caused by gases naturally present in the atmosphere that affect the behaviour of the heat energy radiated by the sun In simple terms, sunlight (shortwave radiation) passes through the atmosphere, and is absorbed by Earth's surface This warms Earth's surface, and then Earth radiates some of The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in Earth's atmosphere Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O), ozone (O 3), and fluorinated gasesGreenhouse gases have very different warming effects one tonne of methane does not have the same impact on warming as one tonne of CO 2Carbon dioxide equivalents (CO 2 e) attempt to convert the warming impact of the range of greenhouse gases into a single metric This is done by multiplying each gas by its 100year 'global warming potential' value the amount of warming



Greenhouse Gas Global Greenhouse Warming




The Greenhouse Effect World101
Methane is the next of the greenhouse gases which has the biggest effect on global warming (15%) This is generated by activities such as livestock production, agriculture, sewage treatment, natural gas and oil distribution , coal mining, fuel use and is also given off from waste tips It lasts an average of 12 years in the atmosphereWHAT IS THE GREENHOUSE EFFECT The greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon and is beneficial for us Certain gases in the atmosphere retain part of the thermal radiation emitted by the Earth's surface after being heated by the sun, this maintains the planet's temperature at a level suitable for the development of lifeGreenhouse Gases Abstract The layer model assumes that the atmosphere acts as a blackbody in the infrared, absorbing and emitting all frequencies of IR light In reality, gases absorb IR light selectively, and most of the gas in the atmosphere doesn't interact with IR light at all The difference can be understood in terms of the effect of



Greenhouse Gases Biology Notes For Igcse 14
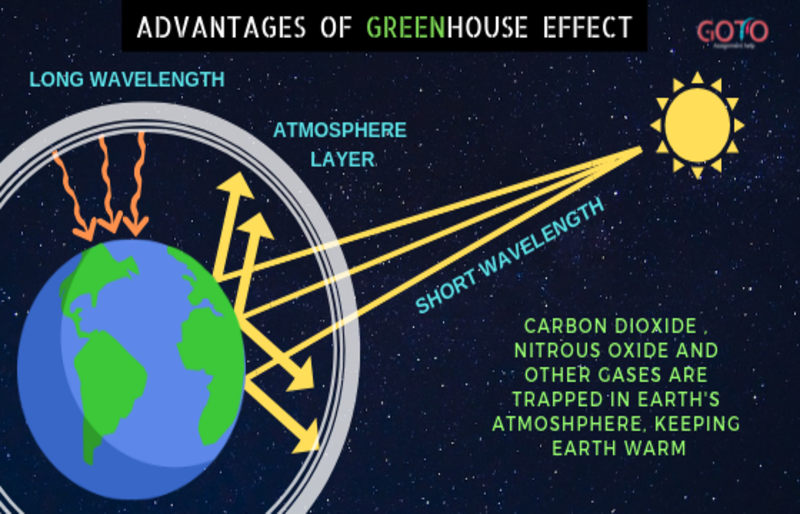



The Advantages Of Greenhouse Effect And The Role Of Greenhouse Gases
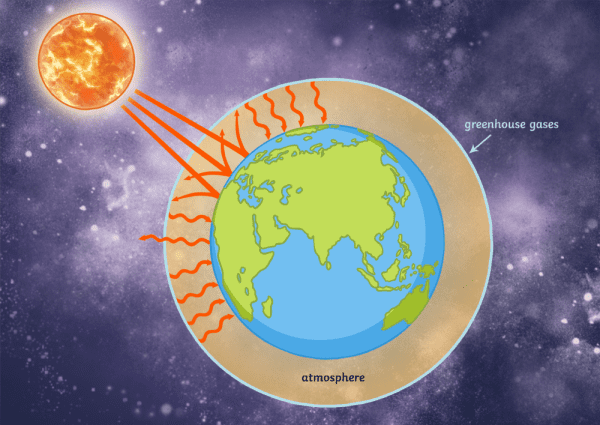
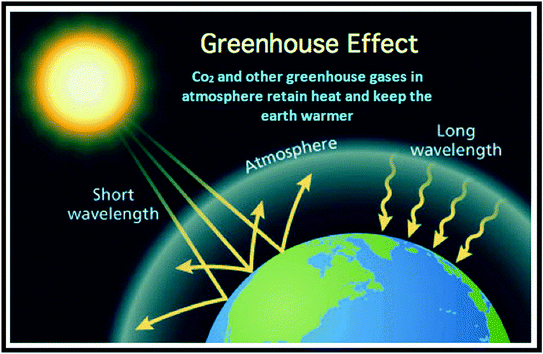
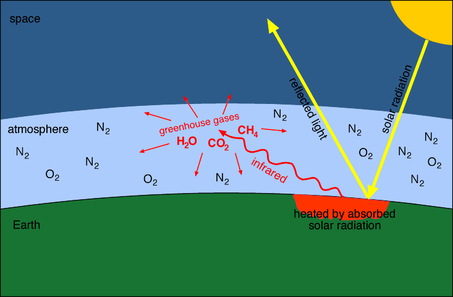
How the greenhouse effect works It's thought that the buildup of greenhouse gases impacts on global temperature in two ways The gases allow more of the sun's rays to enter the atmosphereThe greenhouse effect happens when certain gases—known as greenhouse gases—collect in Earth's atmosphere These gases, which occur naturally in the atmosphere, include carbon dioxide , methane , nitrogen oxide, and fluorinate d gases sometimes known as The Greenhouse Gas Effect The greenhouse effect is a natural process by which some of the radiant heat from the Sun is captured in the lower atmosphere of the Earth, thus maintaining the temperature of the Earth's surface The gases that help capture the heat, called ?greenhouse gases,?




Greenhouse Gases Questions 1 What Is The Greenhouse Effect 2 What Are The 4 Main Greenhouse Gases 3 Why Are Small Amounts Of Greenhouse Gases Good Ppt Download




Greenhouse Gas Effect And Global Warming What Is
Greenhouse gas definition 1 a gas that causes the greenhouse effect, especially carbon dioxide 2 a gas that causes the Learn more An increase in the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases produces a positive climate forcing, or warming effect From 1990 to 19, the total warming effect from greenhouse gases added by humans to the Earth's atmosphere increased by 45 percent The warming effect associated with carbon dioxide alone increased by 36 percentThe greenhouse effect Without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere, the Earth would be about 18°C colder on average than it is now That would make it too cold to support life as we know it




Greenhouse Gases Edexcel Igcse Biology Revision Notes
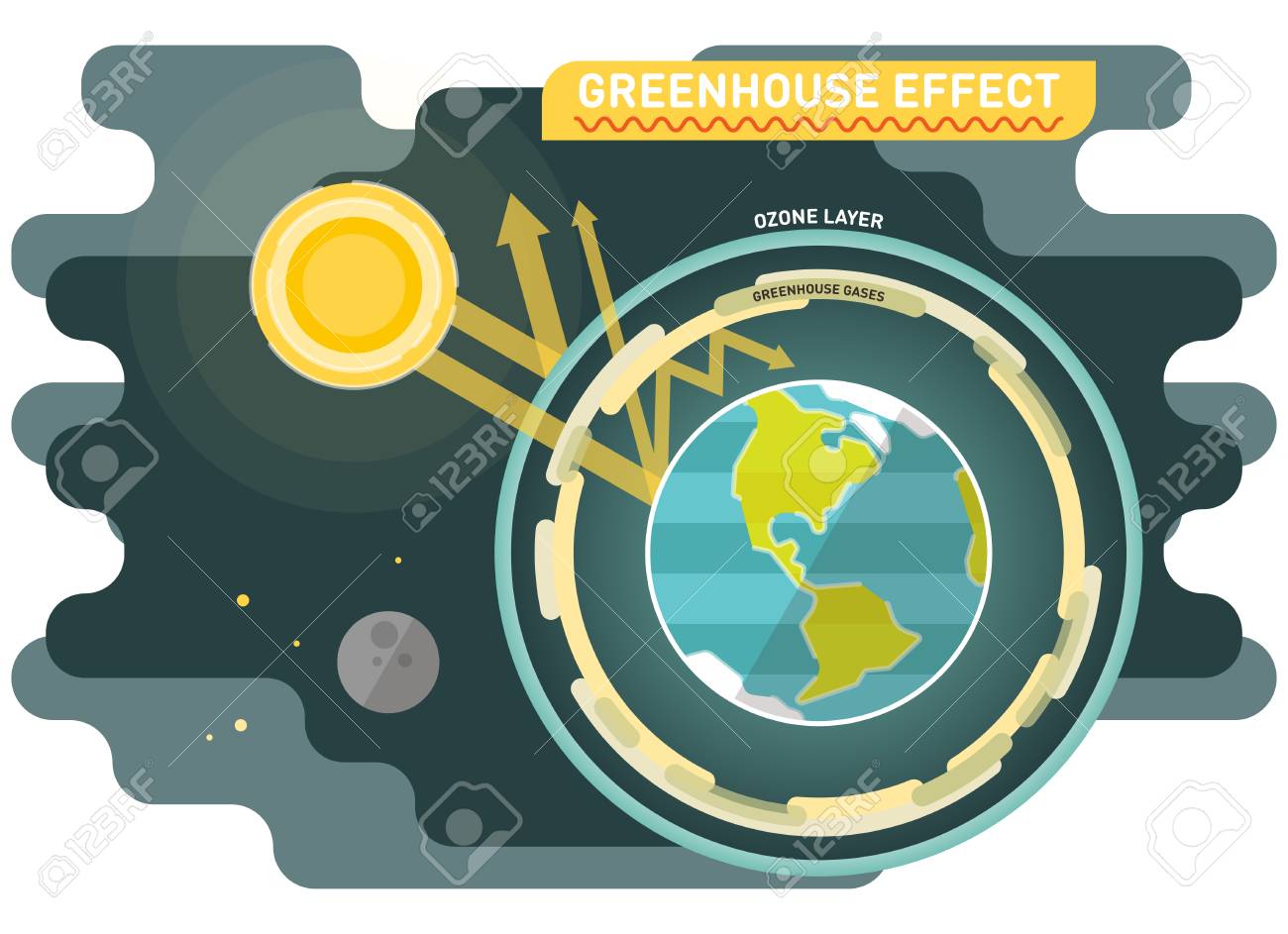



Greenhouse Effect Diagram Graphic Vector Illustration With Sun And Planet Earth With Ozone And Greenhouse Gases Layers Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
For each greenhouse gas, a Global Warming Potential (GWP) has been calculated to reflect how long it remains in the atmosphere, on average, and how strongly it absorbs energy Gases with a higher GWP absorb more energy, per pound, than gases with a lower GWP, and thus contribute more to warming EarthGreenhouse gases that occur both naturally and from human activities include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO 2), methane (CH 4), nitrous oxide (N 2 O) and ozone (O 3) Other greenhouse gases have essentially no natural sources, but are side products of industrial processes or manufactured for human purposes such as cleaning agents, refrigerantsChange the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?



Greenhouse Gases Impact On Environment Iashe




Greenhouse Gas Effect
Change the greenhouse gas concentration and see how the temperature changes Then compare to the effect of glass panes Zoom in and see how light interacts with molecules Do all atmospheric gases contribute to the greenhouse effect?How do greenhouse gases affect the climate? In computerbased models, rising concentrations of greenhouse gases produce an increase in the average surface temperature of the earth over time Rising temperatures may produce changes in precipitation patterns, storm severity, and sea level
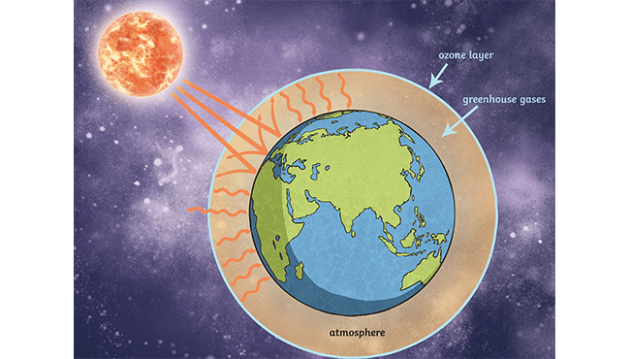



What Are Greenhouse Gases Answered Twinkl Parenting Wiki




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Main Sources Infographic What S Your Impact
The new bulbs keep almost 5 million pounds of carbon dioxide out of the atmosphere each year, reducing greenhouse gas emissions by city government operations by 3 percent The cost of purchasingExplore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds?Explore the atmosphere during the ice age and today What happens when you add clouds?




Greenhouse Effect Infographic Royalty Free Vector Image




Overview Of Greenhouse Gases Us Epa
Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth's surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapor has the largest effect In this lab, you will explore some of the elements that absorb solar energy, the greenhouse gases (GHG) These gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and water vapor You will see that each greenhouse gas responds differently to electromagnetic radiation This is an important asset of our current atmospheric composition The gases that contribute to the greenhouse effect include water vapor, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxides, and chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) On Earth, human activities are changing the natural greenhouse Over the last century the burning of fossil fuels like coal and oil has increased the concentration of atmospheric CO 2
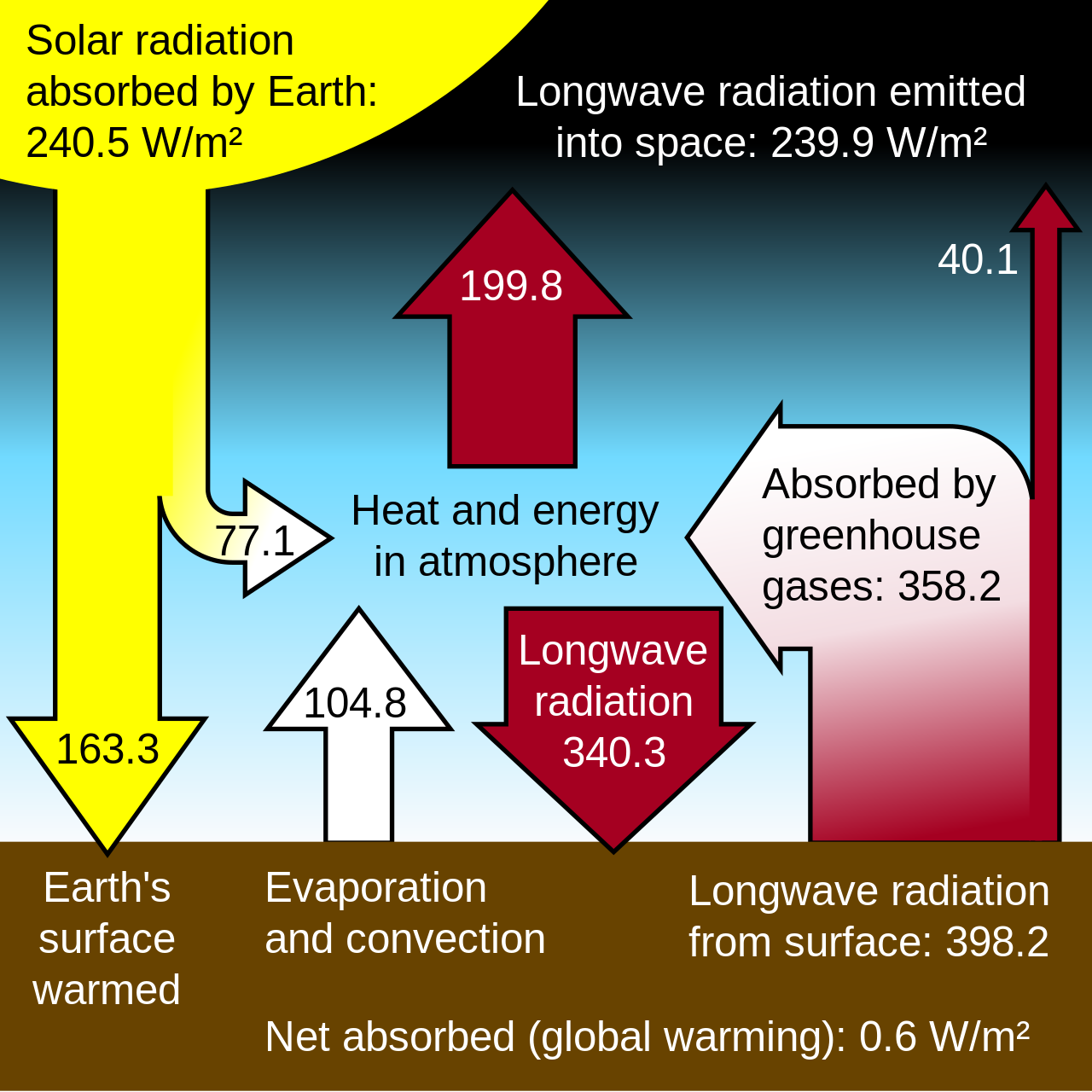



Fajl Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikipedia




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc
Greenhouse effect has been falsified "The influence of socalled greenhouse gases on nearsurface temperature is not yet absolutely proven In other words, there is as yet no incontrovertible proof either of the greenhouse effect, orMIT's Greenhouse Gas Simulator One of a suite of online climate interactive simulations, this Greenhouse Gas Simulator uses the bathtub model to demonstrate how atmospheric concentrations of CO2 will continue to rise unless they are lowered to match the amount of CO2 that can be removed through natural processes
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-474143192-5b7df4fdc9e77c0050c92479.jpg)



Greenhouse Gas Effects On The Economy




What Is Climate Change Climate Assembly




Representation Of The Natural Greenhouse Gas Effect Higher Levels Of Download Scientific Diagram




The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Space Place Nasa Science For Kids




Greenhouse Gases Storyboard Por 24cedbf5




Warm On Top Cold Below Unexpected Greenhouse Gas Effect In Lakes




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Matters




Shutterstock Puzzlepix
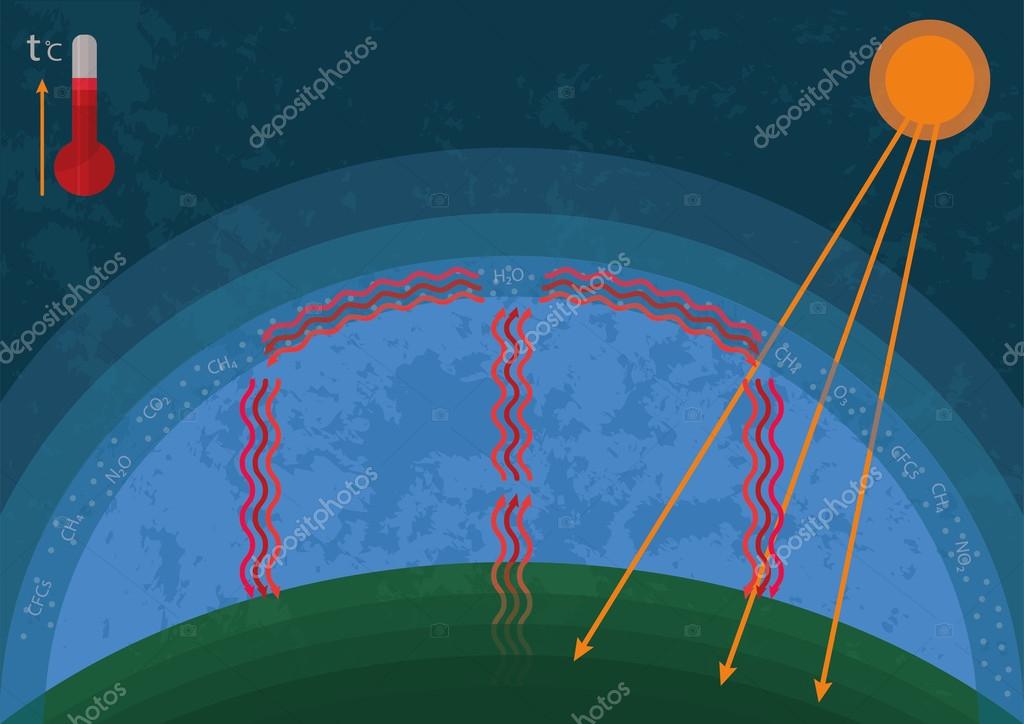



Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Vector Image By C Valentinakru



Rudn University Scientist Showed Global Warmi Eurekalert



The Greenhouse Effect




What Is The Greenhouse Effect Nasa Climate Kids
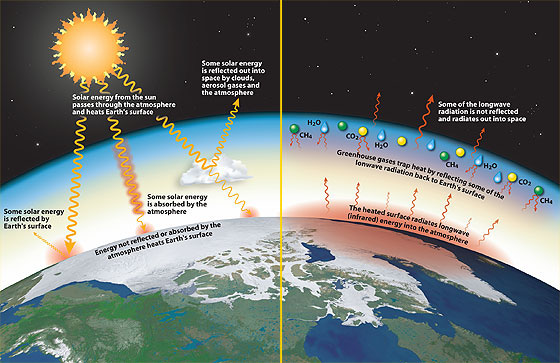



Too Much Of A Good Thing
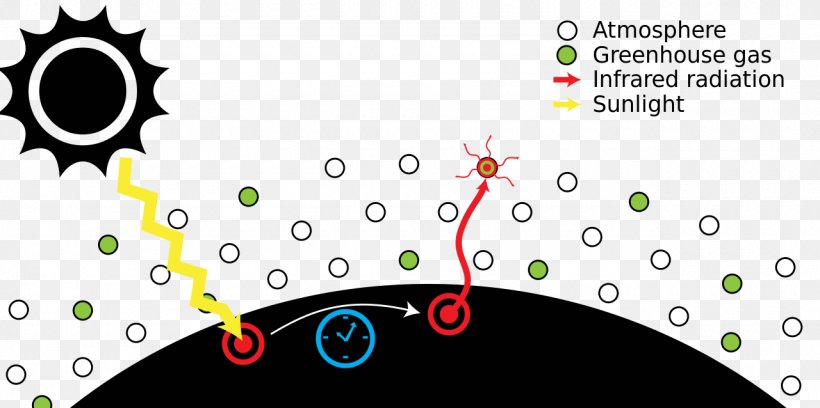



Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Global Warming Png 1280x638px Greenhouse Effect Air Conditioning Atmosphere Of Earth Brand



3




Esrl Global Monitoring Laboratory Education And Outreach



Greenhouse Gases




Carbon Dioxide Methane Nitrous Oxide And The Greenhouse Effect Conservation In A Changing Climate




Greenhouse Effect Wikipedia




Greenhouse Gas Effect By Kavean Gobal




File Greenhouse Gases In Global Warming Effect Gif Wikimedia Commons




What Is Global Warming Global Warming Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gases




Greenhouse Gas Emissions Wikipedia




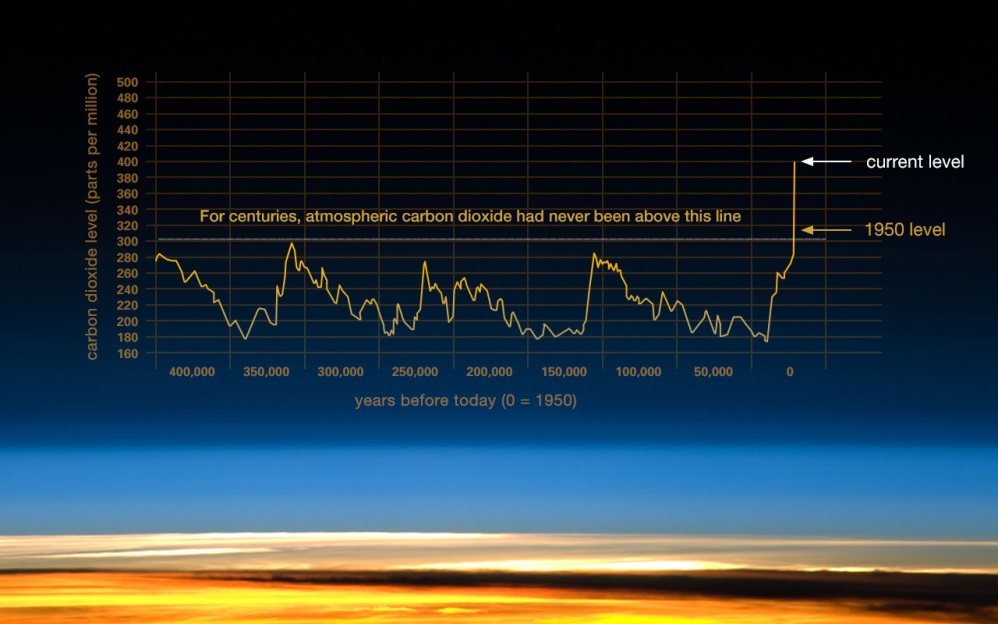
Carbon Dioxide In The Atmosphere Is At A Record High Here S What You Need To Know




Fajl Greenhouse Effect Svg Wikipedia




The Greenhouse Effect Ucar Center For Science Education



1




Practical Guide Greenhouse Gas Emissions Farming For A Better Climate




Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Vector Illustration Of Design Emission




Greenhouse Effect 101 Nrdc




Carbon Cycle And Greenhouse Effect A Scientific Infographic




How To Reduce The Emission Of Greenhouse Gas Shouts




How Greenhouse Gases Influence Climate The Weather Gamut
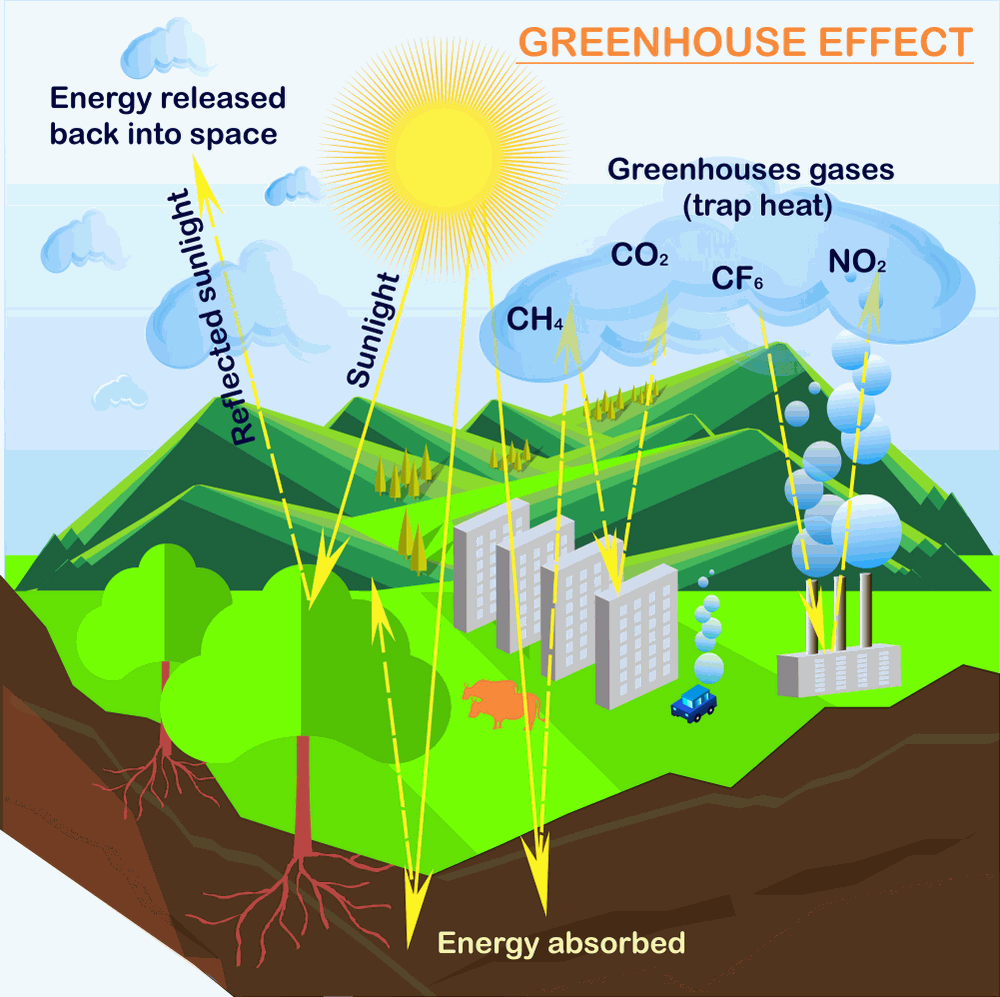



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change Global Warming 19




The Greenhouse Effect




Greenhouse Effect Global Warming Definition Solution Facts
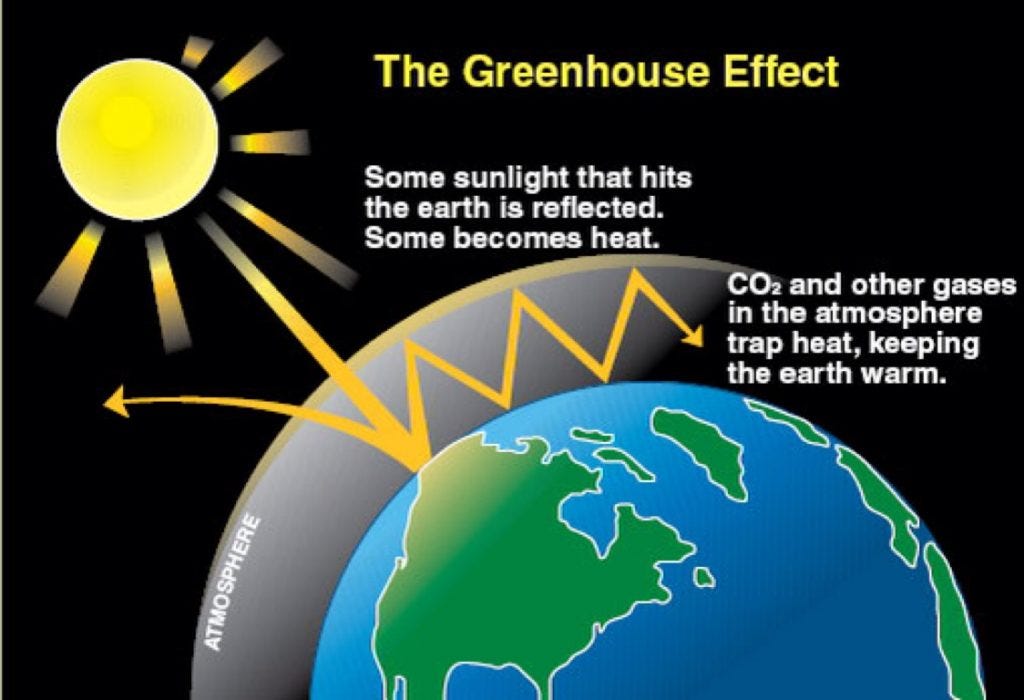



Greenhouse Effect Advantages And Disadvantages By Tutorbin Medium




Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5439 Science Photo Library




Greenhouse Effect Department Of Agriculture Water And The Environment



3 3 Greenhouse Gases Environmental Change Network



3




Earth Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Climate Change Png Clipart Atmosphere Brand Climate Change Earth Earths Energy




Greenhouse Gas Effect Stock Image C033 5440 Science Photo Library




Explainer Global Warming And The Greenhouse Effect Science News For Students




The Greenhouse Effect Fundamentals Of Climate Change Coursera




Greenhouse Gas Effect Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Greenhouse Effect Definition Diagram Causes Facts Britannica




The Greenhouse Effect Cool Australia




The Greenhouse Effect Climate Change




Greenhouse Gases A Student S Guide To Global Climate Change Us Epa



Climate Science Investigations South Florida Energy The Driver Of Climate



Greenhouse Gas Effect Lina Bernal Storyboard




Greenhouse Gases Effects Google Search Greenhouse Gases Effect Greenhouse Gases Greenhouse Effect



1
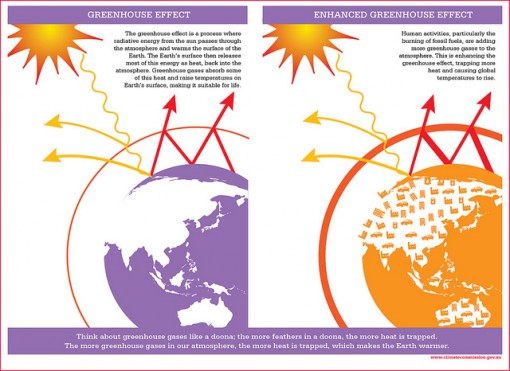



What Is The Greenhouse Effect Conserve Energy Future
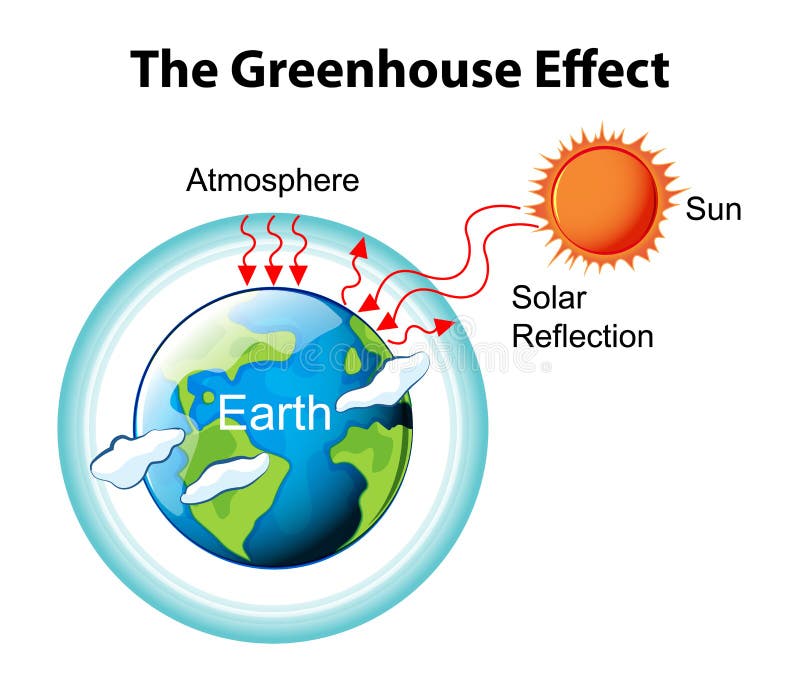



Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations 165 Greenhouse Gas Diagram Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime




15 Sources Of Greenhouse Gases
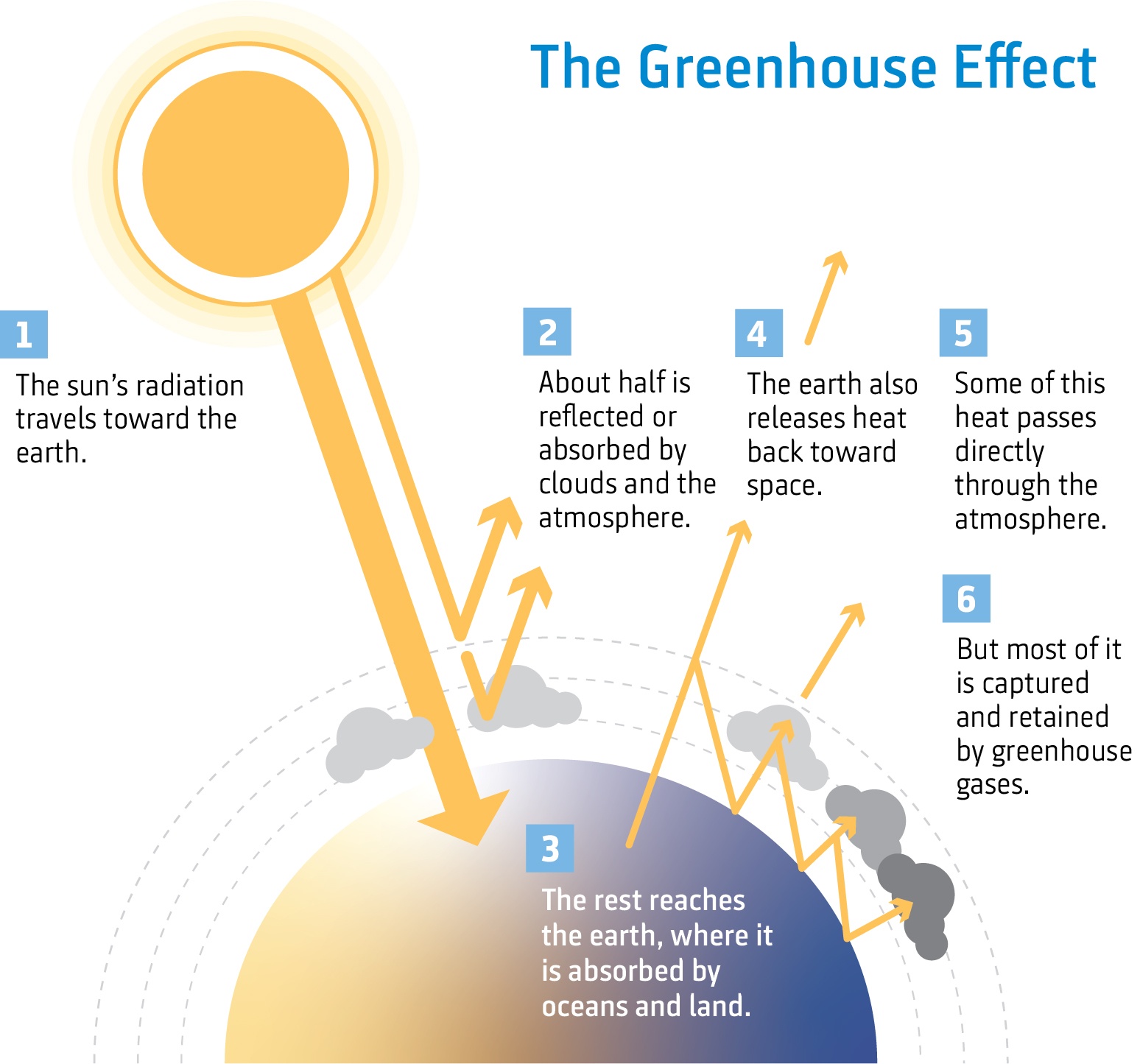



Climate Change The Science Niwa




Greenhouse Gases Causes Sources And Environmental Effects Live Science



Greenhouse Gas Wikipedia




Textbook Representation Of The Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Layer Download Scientific Diagram



Untitled Document




Greenhouse Effect




The Enhanced Greenhouse Effect Geographycasestudy Com




The Greenhouse Effect Niwa




Greenhouse Gases U S Energy Information Administration Eia




Climate Change And Greenhouse Gas Emissions City Of Lakewood




Schematic Of Greenhouse Gas Effect 8 Download Scientific Diagram
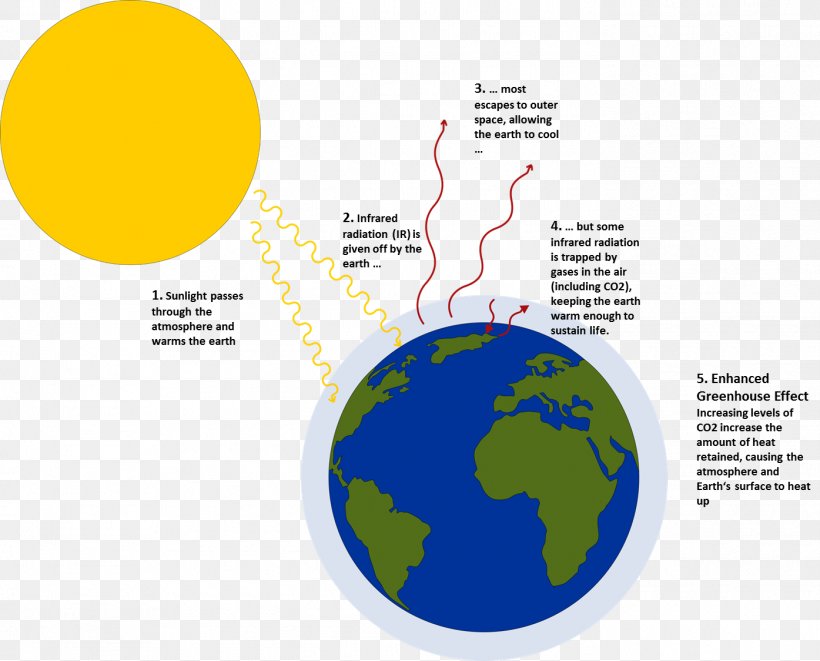



Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Global Warming Png 1395x1125px Greenhouse Effect Area Atmosphere Atmosphere Of Earth Brand




The Greenhouse Effect Download Scientific Diagram




What You Need To Know About Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming By Psc Solar Linkedin
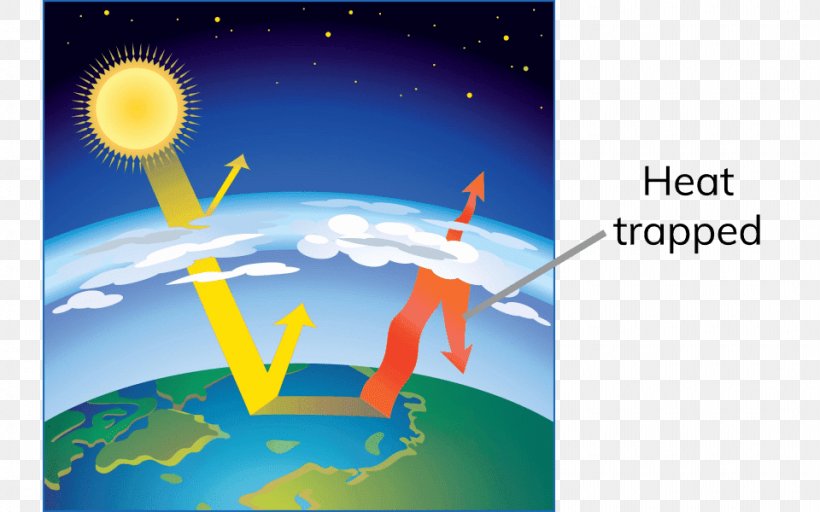



Earth Greenhouse Effect Greenhouse Gas Atmosphere Png 960x600px Earth Atmosphere Atmosphere Of Earth Brand Climate Download
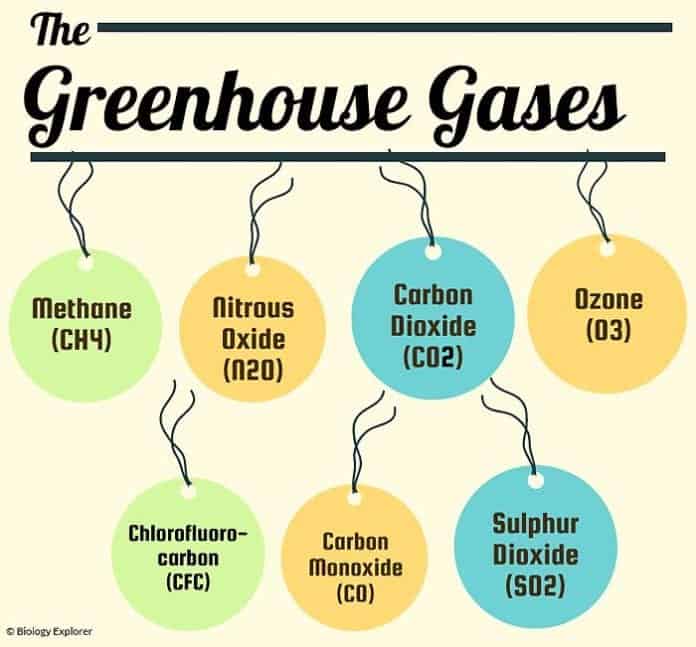



Types Of Greenhouse Gases Definition And Effects On Climate Change




The Greenhouse Effect M 3 Global Issues The




The Greenhouse Effect British Geological Survey




Diagram Of The Greenhouse Gas Effect Download Scientific Diagram




What Is A Greenhouse Effect And Why Does It Exist
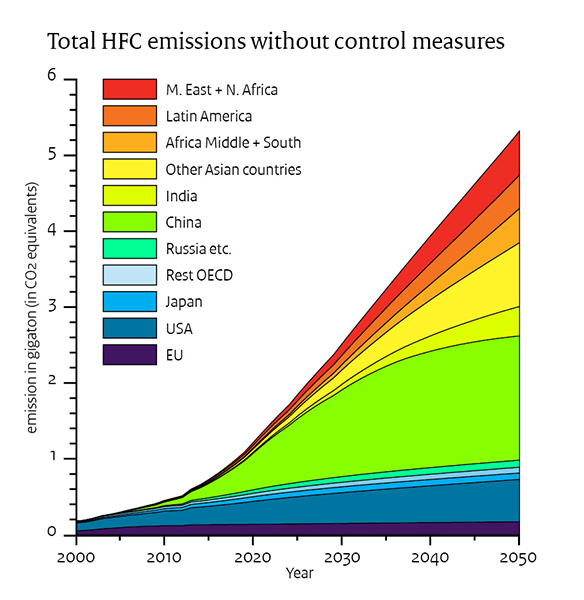



Contribution Of Hfcs To The Greenhouse Effect Rivm




Specific Interpretations Greenhouse Gases 101 Sustainability
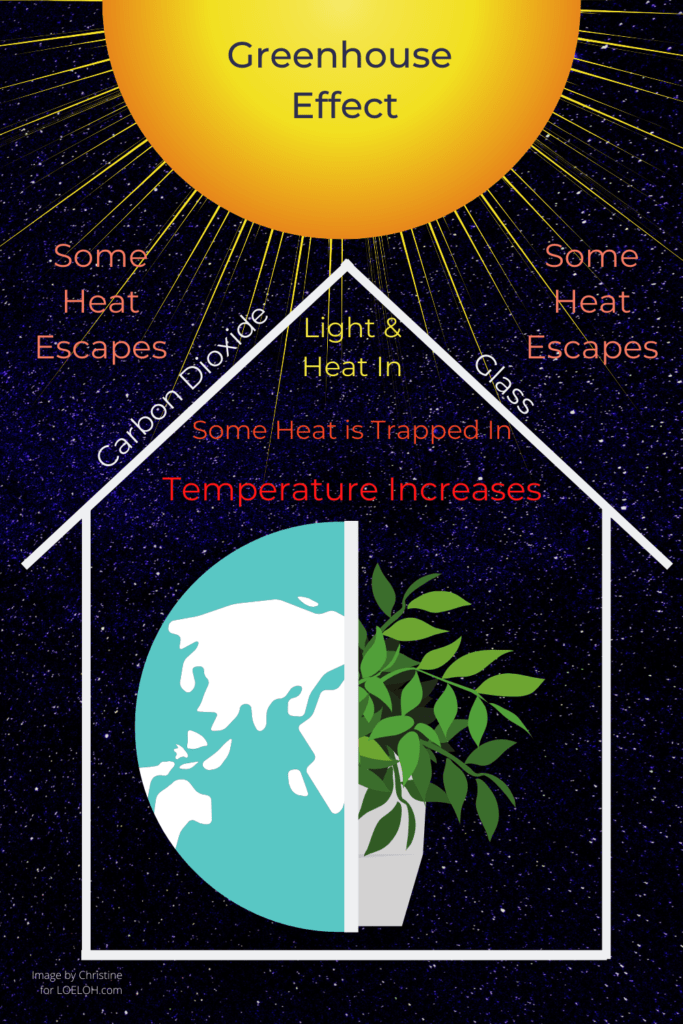



How Are Carbon Dioxide And Climate Change Connected Love Our Earth Love Our Home



What Is The Green House Effect Rising Sea Level




Greenhouse Effect And Greenhouse Gases Youtube
コメント
コメントを投稿